Structural identifiability algorithms & software
- Date: April 30, 2015
- People: Nikki Meshkat (nicolette.meshkat[at]gmail.com), Christine Kuo (ckuo24[at]gmail.com)
- Keywords: keywords
- Website
The COMBOS Web App
Parameter identifiability problems can plague modelers during model quantification, even for relatively simple models. Structural identifiability (SI) is the primary question, usually understood as knowing which of P unknown biomodel parameters p1,…, pi,…, pP are – and which are not – quantifiable in principle from particular input-output (I-O) biodata. It is not widely appreciated, however, that the same data-base also can provide quantitative information about the structurally unidentifiable (not quantifiable) subset, in the form of algebraic relationships among (combinations of) unidentifiable pi. Importantly, this is a first step toward finding what else is needed to quantify particular unidentifiable parameters of interest – possibly even all parameters – e.g. from new I-O experiments. We’ve developed novel algorithms that address and solve the SI problem for a practical class of nonlinear (and linear) ordinary differential equation (ODE) systems biology models, and implemented them as a user-friendly web application (app) – COMBOS. Users provide the structural ODE and output measurement models in one of two standard forms. COMBOS provides a list of uniquely (globally) and non-uniquely (locally) SI model parameters, and – importantly – the combinations of parameters not individually SI. If locally SI, it also provides the number of different solutions – also with important implications in practice.
The behind-the-scenes symbolic differential algebra algorithm is based on computing Gröbner bases of model attributes established after some algebraic transformations, all using the computer algebra system Maxima. Built-in examples include unidentifiable 2 to 4-compartment models and an HIV dynamics model.
COMBOS was developed for facile instructional and research use. We use it in the classroom to illustrate SI analysis; and also have simplified complex models of tumor suppressor p53 and hormone regulation – based on explicit computation of parameter combinations.
The COMBOS web app user interface. (a) Header, user instructions and placeholder for user model – if already available in a file. 
Figure a
(b) Interactive model entry illustrating a 4-compartment nonlinear HIV model example with one experimental input and 2 output measurements. Equations are entered using familiar math programming language and translated on the right into natural math (“pretty”). Six additional example models are selectable on the interface, to familiarize users with the app and its features.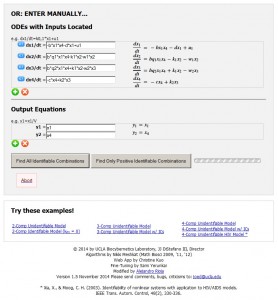 Figure b
Figure b
(c) Structural identifiability (SI) analysis results provided in ~32 secs; 2 individual and one product of 9 SI combos are shown uniquely SI; 4 remaining product or sum combos of other 7 parameters are shown to have three feasible solutions each. The Model in Copy/Paste Format can be readily used to run variations of this model, using the copy/paste input window shown in (a). 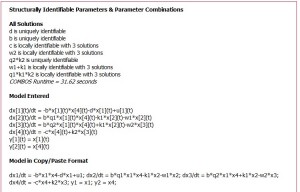 Figure c
Figure c
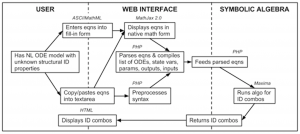
Flow chart of information flow in COMBOS. HTML and ASCIIMathML are utilized in the user section; the web interface is written in PHP and MathJax 2.0; and the symbolic algebra is done in Maxima, ported via PHP.